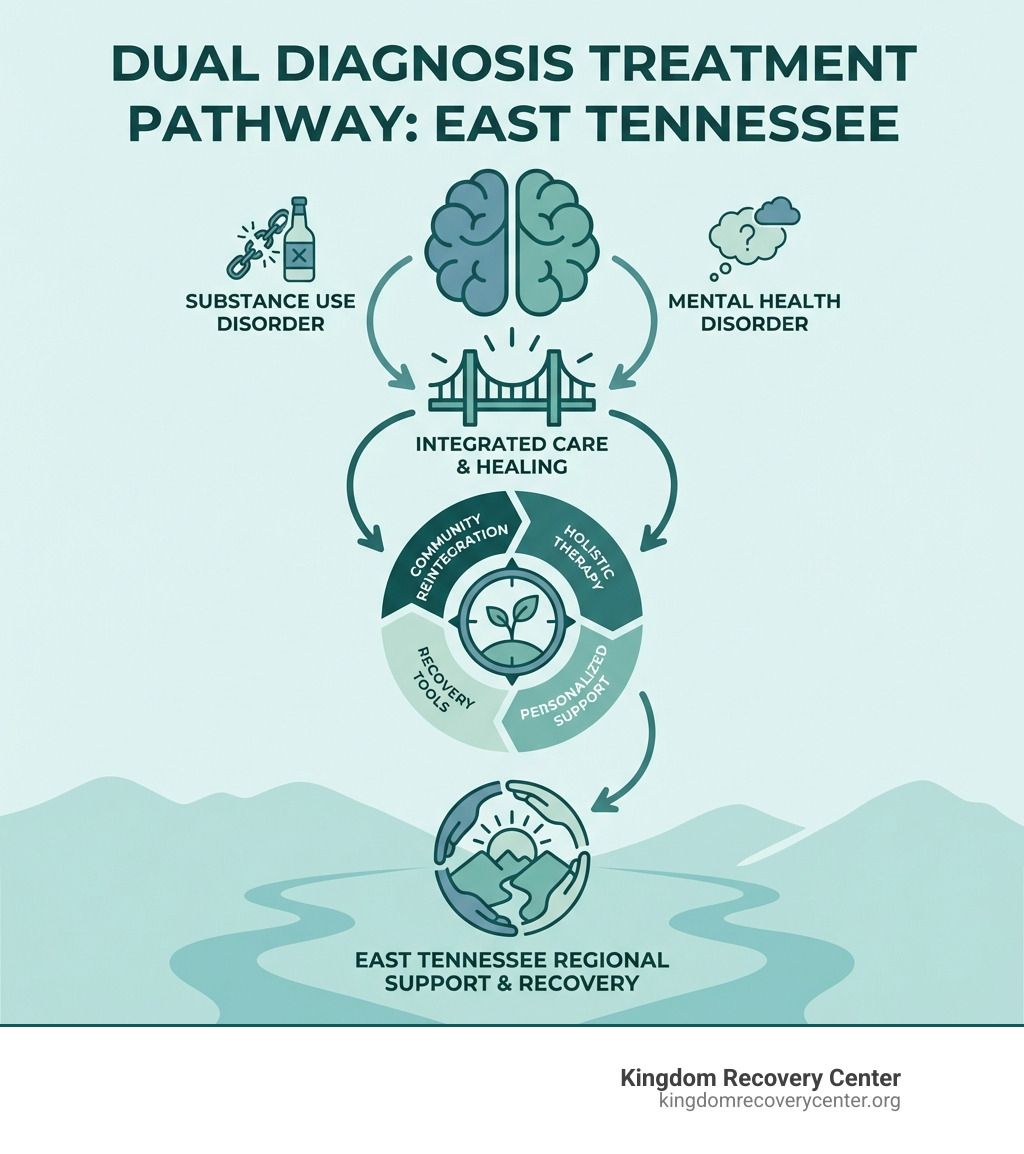
Understanding the Interrelationship of Mental Health and Addiction
Is managing mental health issues alongside addiction a constant challenge? This post explains the relationship between mental health issues and addiction while offering insights into recognizing co-occurring disorders and exploring dual diagnosis treatment. Readers will find clear explanations, signs of co-occurring disorders, and effective strategies for management. The content addresses concerns about a lack of understanding regarding integrated treatment benefits, helping professionals and individuals make informed decisions toward recovery.
Key Takeaways
- early identification of mental symptoms improves treatment outcomes
- integrated care reduces challenges from co-occurring disorders
- collaboration among professionals creates targeted intervention strategies
- family and peer support enhance recovery and reduce relapse risks
- evidence-based therapies combine medication management and holistic techniques
The Interrelationship of Mental Health and Addiction

Mental health plays a critical role in substance use, with research underscoring the impact of bipolar disorder and other conditions. The experience of these challenges may influence the disease dynamics of addiction. Contingency management and insurance strategies provide practical insights into the link between mental health issues and substance use, setting the stage for detailed discussion.
Identifying the Link Between Mental Health and Substance Use
Research indicates a strong connection between mental challenges and substance use, particularly when a patient exhibits symptoms of a disorder that affects daily functions. Clinics often observe that fear linked to worsening mental health may reduce adherence to treatment protocols, creating obstacles in managing substance use effectively.
Providers note that early identification of mental symptoms plays a significant role in addressing the cycle of substance use. The collaboration between mental health professionals and clinic staff ensures that patients receive targeted care, overcoming the fear associated with their condition and promoting better adherence to therapeutic plans.
How Mental Health Issues Contribute to Addiction
Clinical observations indicate that individuals facing mental health challenges often struggle with irritability and anxiety, which may increase reliance on substances. This difficulty with stress management can hinder efforts in therapy, reducing the likelihood of achieving sustained abstinence.
Experts note that incorporating peer support can alleviate the tension associated with mental health issues, creating opportunities for early intervention in addiction. Coordinated care that addresses stress management and uses therapy as a core element promotes a more effective recovery process and reduces overall irritability.
Understanding Co-Occurring Disorders

The section covers defining co-occurring disorders and their implications, providing insight into lifestyle impacts and clinical observations in California regarding methamphetamine use. It also highlights common examples of mental health and addiction disorders, detailing the behavior and pain challenges patients face, setting the stage for focused discussion on identifying and managing these intertwined issues.
Defining Co-Occurring Disorders and Their Implications
The assessment of co-occurring disorders focuses on conditions such as schizophrenia and mood disturbances, which directly impact the mind and may require coordinated care approaches. The american medical association supports research that links severe mental health challenges with the misuse of substances like stimulant drugs, emphasizing the need for early intervention and integrated treatment plans.
Clinical practice reveals that individuals grappling with co-occurring disorders face significant hurdles in managing both mental health symptoms and addiction. Specialized treatment strategies address these issues by tailoring therapeutic plans that consider conditions like mood disorders and schizophrenia, offering structured support for recovery while minimizing the use of stimulant drugs.
Common Examples of Co-Occurring Mental Health and Addiction Disorders
Clinical research highlights several frequent examples of co-occurring mental health and addiction disorders, such as conditions involving conduct disorder and anxiety issues that affect daily memory functions. These assessments support targeted programs designed to improve screening processes and provide effective treatment for patients struggling with intertwined issues.
Case studies indicate that early intervention is key, with specialized initiatives incorporating 988 support systems to address simultaneous challenges. This approach offers practical insights into managing co-occurring conditions while reinforcing the importance of thorough screening and personalized programs for lasting recovery.
The Role of Dual Diagnosis Treatment

This section covers integrative approaches in dual diagnosis treatment, highlighting the benefit of addressing mental health and addiction simultaneously. Practical strategies, including exercise and coordinated care by a physician, support a stable heart and mind. The discussion extends to timely diagnosis and the impact of domestic violence in treatment plans, offering clear, actionable insights for targeted recovery.
Integrative Approaches in Dual Diagnosis Treatment
This approach combines clinical best practices with practical strategies to address both mental health and addiction challenges. Providers integrate medication management with personalized coping techniques designed to reduce impulsivity and help patients navigate peer pressure effectively.
Experts monitor treatment through rigorous verification-of-benefits to ensure patients receive coordinated dual diagnosis support. They use targeted interventions that blend structured medication protocols with actionable coping strategies addressing impulsivity and the effects of peer pressure.
Benefits of Addressing Both Disorders Simultaneously
Addressing both mental health and addiction simultaneously leads to improved outcomes by reducing overall stress and streamlining patient care. Integrated dual diagnosis treatment in primary care settings helps reduce relapse rates and improve recovery by ensuring that patients in regions such as Florida receive comprehensive care that reflects the true prevalence of co-occurring disorders and what-we-treat effectively.
This approach allows clinicians to monitor recovery progress closely and tailor treatment plans to individual needs:
- Early identification of stress factors
- Personalized intervention strategies
- Enhanced support through primary care services
- Reliable data on prevalence and treatment success
Such coordinated care enhances patient engagement and fosters lasting recovery through a collaborative treatment model.
Symptoms of Co-Occurring Disorders

Recognizing signs of mental health issues alongside addiction involves assessing the risk of opioid use disorder, insomnia, and fluctuating mood patterns. The content distinguishes between addiction symptoms and mental health signals, including variations based on gender. Insights highlighted on linkedin indicate practical approaches to manage these overlapping challenges effectively.
Recognizing Signs of Mental Health Issues Alongside Addiction
The interrelationship between mental health and addiction emerges when a patient presents signs such as mood instability coupled with increasing reliance on substances like benzodiazepine and prescription drug addiction, often rooted in adverse childhood experiences. These indicators may point to overlapping challenges; early attention to these signs improves treatment outcomes:
| Indicators | Observations |
|---|---|
| Mood Changes | Fluctuations in mood may signal underlying mental health issues. |
| Substance Dependence | Increased use of prescription drugs and benzodiazepine suggests co-occurring disorders. |
| Background History | Adverse childhood experiences can contribute significantly to these challenges. |
Clinicians note that recognizing these patterns helps tailor a patient’s treatment plan, offering structured support that addresses both mental health concerns and addiction issues. Such proactive measures enable practitioners to guide patients toward recovery by refining interventions and monitoring progress in managing behaviors associated with prescription drug addiction and the aftereffects of adverse childhood experiences.
Distinguishing Between Addiction Symptoms and Mental Health Symptoms
Experts in social work and hospital settings in New Jersey observe that distinguishing between addiction symptoms and mental health symptoms requires careful analysis of behavioral patterns, physical cues, and changes in daily functioning. Detailed assessments using a comprehensive database enable clinicians to recognize whether a patient’s challenges stem primarily from substance dependence or underlying mental health issues, thereby guiding personalized treatment strategies.
Clinicians working in community settings emphasize that early identification of overlapping signs is crucial for effective intervention. Drawing on first-hand experiences from social work and hospital care in New Jersey, professionals use database-driven insights to tailor solutions that address both mental health challenges and addiction, ensuring that individuals receive focused care that meets their unique needs.
Effective Strategies for Management

This section examines evidence-based therapies for dual diagnosis and holistic techniques to support recovery. It outlines how structured email follow-ups and antidepressant management are integrated into clinical trial protocols to combat social isolation and improve overall health. The upcoming details offer practical insights into connecting mental health and addiction treatment effectively.
Evidence-Based Therapies for Dual Diagnosis
Evidence-based therapies for dual diagnosis aim to reduce issues related to substance abuse and improve treatment outcomes for patients with overlapping challenges. The approach uses targeted interventions involving medicine and structured monitoring to help patients manage behaviors linked to amphetamine use, ultimately building sustainable habits.
Clinical practitioners highlight practical case studies that support the integration of therapies addressing both mental health concerns and substance abuse patterns. This method involves regular assessments to control nausea and other side effects of medicine, thus reinforcing patient commitment to overcoming detrimental habits.
Holistic Techniques to Support Recovery
The integrated approach in dual diagnosis care includes embracing holistic techniques that reduce loneliness and direct attention toward improving overall well-being. Providers in health care settings note that incorporating mindfulness exercises and community support groups empowers individuals to maintain sobriety while alleviating feelings of isolation:
| Holistic Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Mindfulness Practices | Improves mental clarity and reduces loneliness |
| Community Support | Maintains sobriety through shared experiences |
| Physical Activity | Enhances overall health care outcomes |
Specialized professionals advocate for straightforward strategies that offer both immediate comfort and long-term recovery support. They illustrate through practical examples how structured routines and collaborative health care practices assist patients in managing the feeling of isolation while strengthening their path to sustained sobriety.
Building a Supportive Environment

Family and friends play a crucial role in recovery by supporting motivation and emotional stability, aiding in the management of co-occurring challenges including hepatitis b and sud. This section outlines practical strategies for leveraging personal support and accessing resources to handle dual diagnosis issues effectively, setting the stage for a detailed discussion on building a supportive network.
How Family and Friends Can Aid in Recovery
Family and friends play an important role in smart recovery by providing practical support and emotional reassurance to those dealing with substance dependence. They help mitigate risk factors that may worsen mental health challenges and addiction, while statistics from Maryland highlight how community backing can lower relapse rates.
Close contacts can offer actionable insights that simplify recovery efforts and encourage adherence to treatment plans. Their direct involvement serves as a stabilizing factor during difficult times, ensuring that supportive environments promote resilience against risk factors associated with mental health issues and substance dependence.
Resources for Managing Dual Diagnosis Challenges
Clinical professionals emphasize the importance of accessing local resources and support groups in the United States, where guidance on managing dual diagnosis challenges is readily available. Practical insights from expert providers show that addressing panic symptoms and alcohol use, along with consistent monitoring to prevent relapse, can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Specialized centers offer comprehensive care programs that consider the combined impact of mental health issues and addiction, including genetic factors related to a gene predisposition for alcohol use disorder. Experienced practitioners recommend practical strategies to reduce panic episodes and monitor relapse risks, thereby empowering patients to maintain stability within their communities.
Conclusion
Understanding the complex relationship between mental health and addiction is crucial for providing effective, integrated care. Recognizing the intertwined nature of these issues helps clinicians tailor treatment plans that address both problems simultaneously. Coordinated care and early identification empower providers to improve treatment outcomes and reduce relapse rates. This knowledge equips families, friends, and professionals with the tools needed to support sustained recovery and overall well-being.